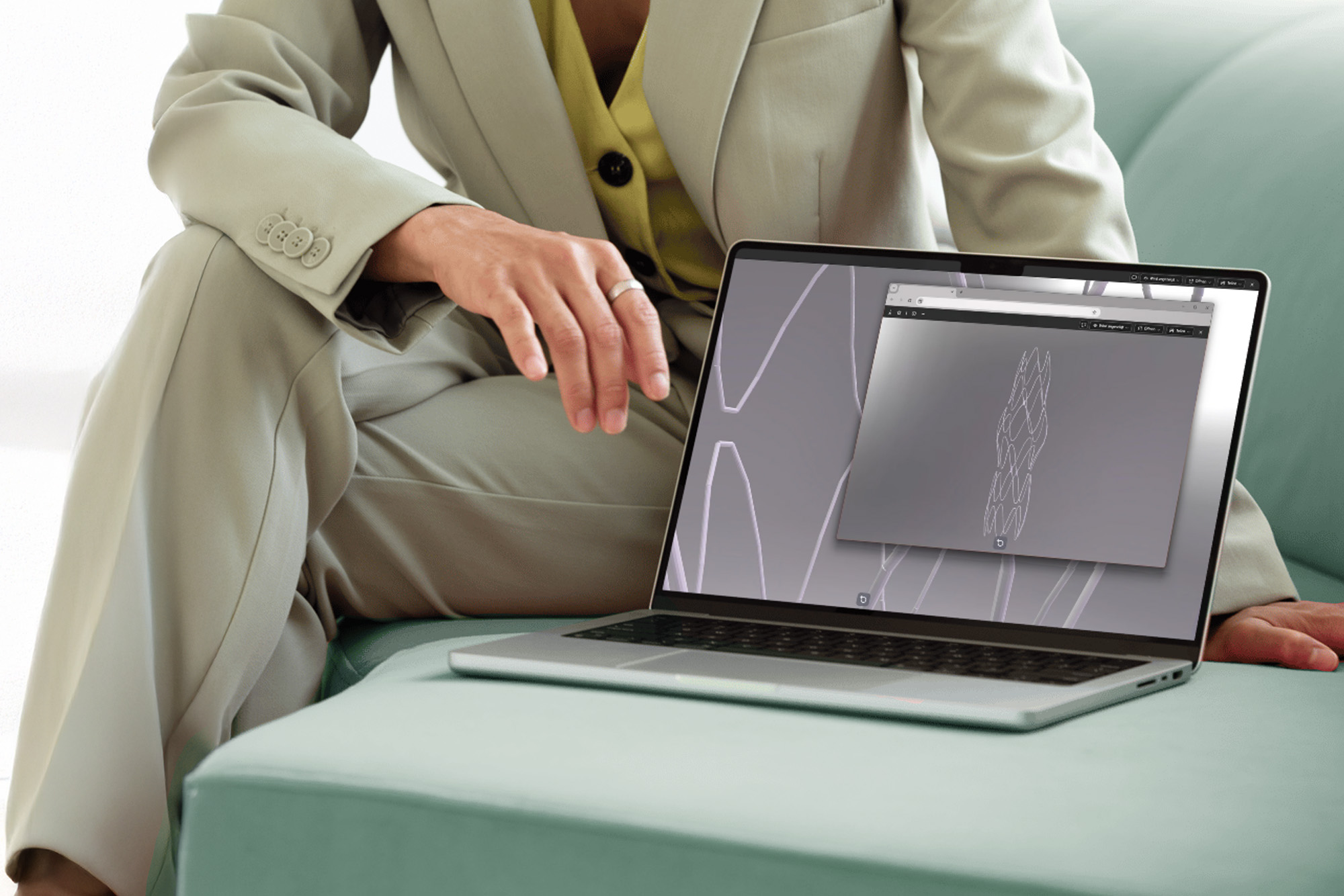
The challenge: when every aneurysm is unique
Bifurcation aneurysms are one of the greatest challenges of modern neurosurgery. They occur at vascular bifurcations in the brain, where several blood vessels cross and divide, creating areas that are anatomically extremely different. Standardized stents reach their limits here.

Every patient, every vascular structure, every aneurysm is different. The vision of the IndiPlant project: a system that uses medical image data to design a customized stent for each individual vascular situation – and validates it through simulation and 3D printing.
The vision: AI as a pioneer of personalized medicine
In the long term, IndiPlant is to be developed into a complete system that enables patient-specific treatments, not only in the brain, but also for other areas of the body in the future. “We are working on a solution that can create the basis for truly personalized vascular therapy,” explains Sebastian Wittor, project manager at BAYOOMED.
The technology combines medical image processing, artificial intelligence, simulation and 3D printing – in an end-to-end digital process.
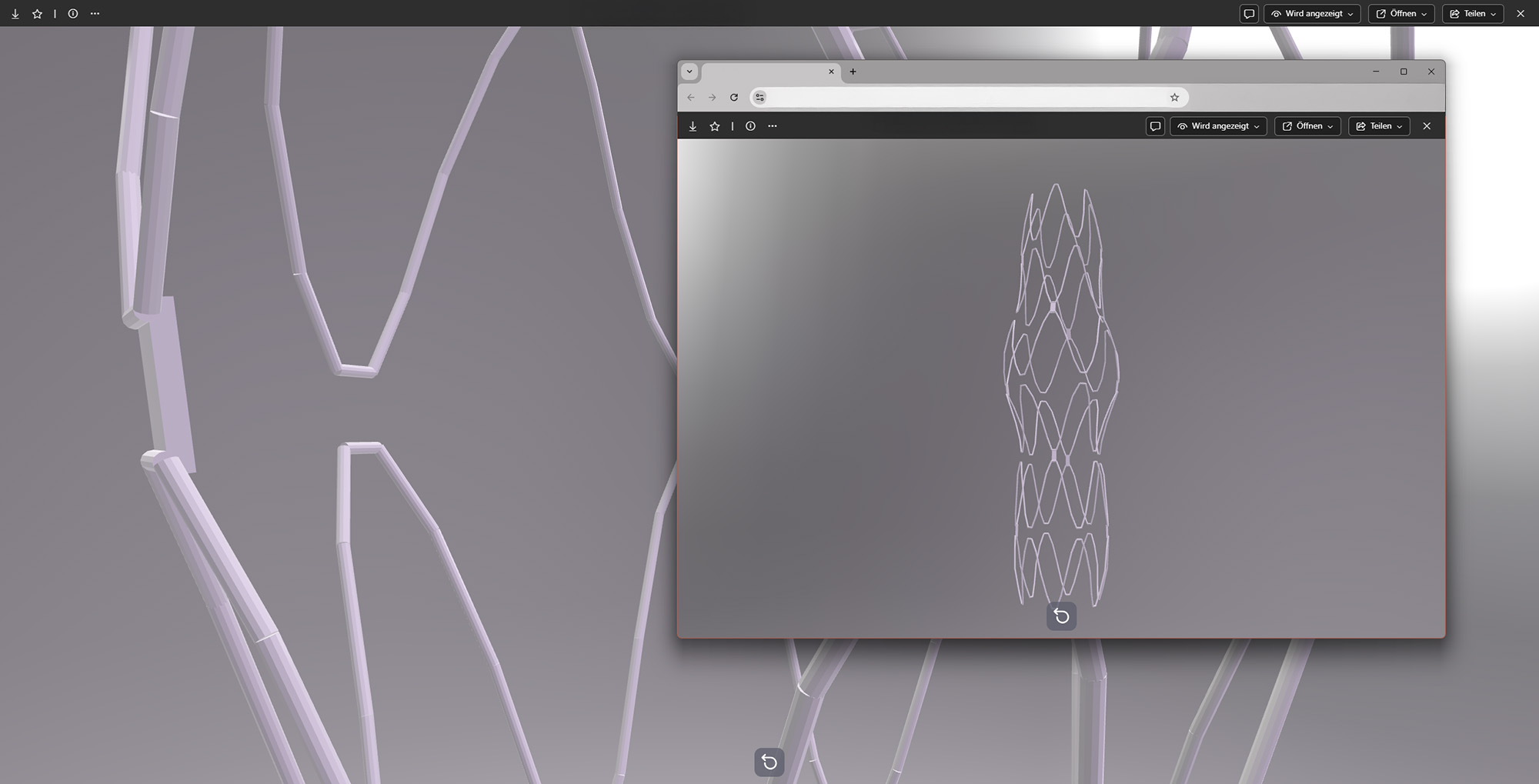
The role of BAYOOMED GmbH: AI at the heart of the system
BAYOOMED is responsible for the development and training of the AI system within the consortium. The model analyzes MRI and CT data (DICOM), creates a 3D model of the aneurysm including the vascular environment and generates an individual stent design from this. The special thing about this is that validation is not only carried out on the finished product, but is process-based through simulations of the AI-generated design.
This means that it is not the stent that is tested, but the entire process of its formation that is validated – an approach that is unique in medical technology to date.
The path: from research to clinical relevance
BAYOOMED initially received DICOM data from Jena University Hospital. This first had to be carefully processed. This was a complex process, as vessels are flexible, change minimally due to blood pressure and can only be visualized with the help of contrast agents.
The team then used various pre-processing methods. It proved to be a decisive success factor, with around 60% of the total effort going into this phase. A combination of U-Net architecture, MONAI framework and PyTorch was used in the training. With an initially tiny database of just five aneurysms, the overall process was tested and then the database was expanded to 60 and later 128 cases.
As a result, model accuracy increased from 42% to 85% accuracy, a huge improvement in just a few months.
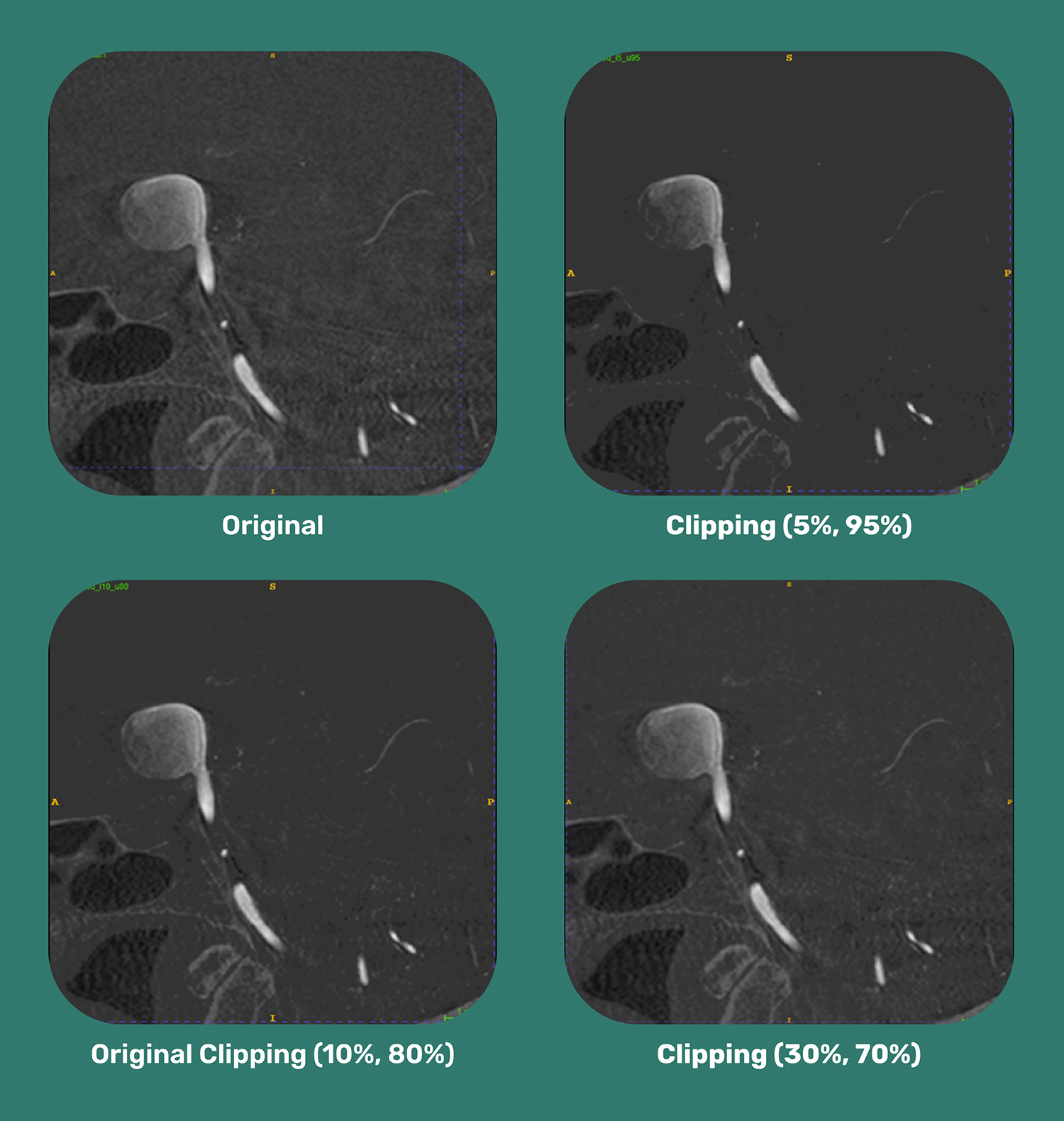

Prepocessing - Denoising
Erhöhung der Qualität der Bilder durch Clipping als Lösung um Rauschen zu reduzieren.
Agile research instead of a classic project plan
In contrast to traditional medical product development, the team worked in an open-ended and exploratory manner. Instead of a fixed backlog, the focus was on research, paper research and technical iterations.
“We had to develop the right tools, libraries and algorithms ourselves over the course of the project,” explains Sebastian Wittor. “It was research-driven work in the best sense of the word, with the freedom to test and reject hypotheses and explore new avenues.” This also gave rise to the idea of a visual user interface to better interpret and validate the results of the AI, a step that was born out of practical experience.

“It was research-driven work in the best sense of the word, with the freedom to test and reject hypotheses and explore new avenues.”
Sebastian Wittor, Project Manager at BAYOOMED
Findings from the project
The work on IndiPlant has provided BAYOOMED with valuable insights for future AI developments:
Results and outlook
Today, the entire IndiPlant process can be mapped digitally – from data acquisition, AI-based segmentation and stent creation to simulation and 3D printing of the finished stent.
The next steps: optimization of the individual process steps, better coordination of the systems involved and further development of the AI. The research project will run until the end of 2026, with the aim of reaching the preclinical phase with the long-term goal of bringing the system to market maturity.
Conclusion: A new era of MedTech innovation
IndiPlant shows what is possible when research, technology and medicine come together. BAYOOMED is not working on an app or software, but on a fundamentally new approach to patient-specific medical devices.
“Working on a system that lays the foundation for personalized vascular therapy is fascinating,” says Sebastian Wittor, “We are actively shaping the future of medical technology here and that is an incredibly motivating feeling.”

